The Customer
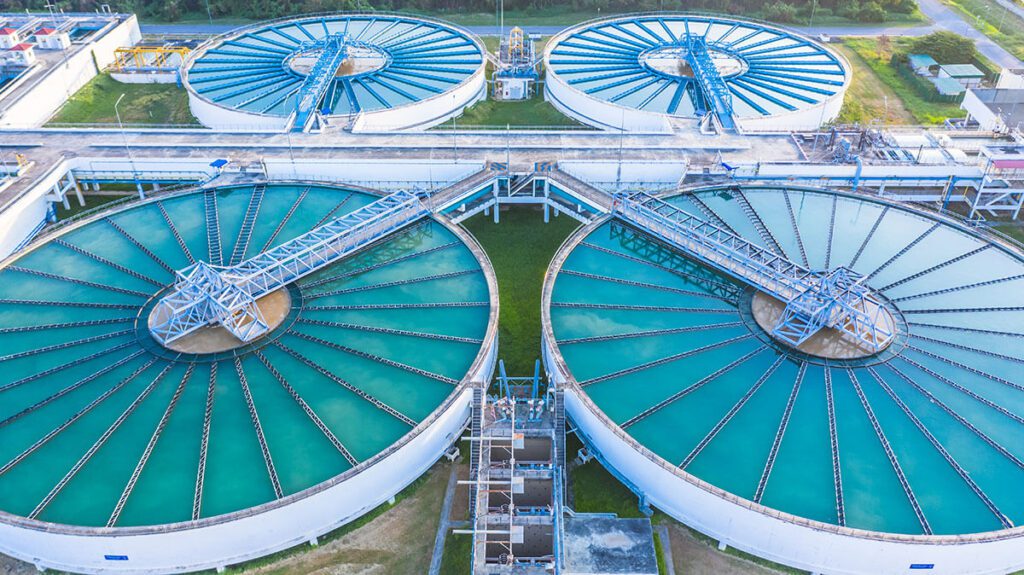
19 MGD conventional treatment facility treating river water source in southern U.S., serving over 50,000 customers
Plant experienced recurring pH problem at least 3-4 times during summer months when low alkalinity conditions set in. Partnering with GTI helped identify and treat seasonal alkalinity problem with new coagulant.
The Challenge
Seasonal low alkalinity water conditions
The water treatment plant experienced a reoccurring pH problem at least three to four times during the summer months when low alkalinity conditions set in.
Aluminum sulfate in the traditional alum water treatment program further compounded the problem by consuming alkalinity and reducing pH below the plant’s 6.0 limit.
Collaborative Innovation
Customer partnered with GTI to identify proper treatment solution
- Joint discovery of seasonal alkalinity problem
- Identification of new coagulant to prevent alkalinity issue while maintaining compliance with established regulatory guidelines and optimizing critical treatment parameters
The Solution
Switched from aluminum-based (alum) chemistry to Polyaluminum Chloride (PACl) coagulation chemistry, resulting in
- Lower consumption of alkalinity
- Improved effectiveness over broader pH range
- Reduced chemical dosage and chemical costs within treatment process
- Lower residual aluminum levels in treated water
- Improved treated water quality, including lower TDS and sulfate levels
- Lower sludge production
- Reduced need for post-treatment pH adjustments using lime, thereby improving capital costs, operating conditions and maintenance requirements

Dose (ppm) in Different Raw Water Conditions – Alum vs GPAC 2350